The age-old question of whether to rent or buy a home continues to be a complex and deeply personal decision. Weighing the pros and cons of renting vs buying requires careful consideration of your individual financial situation, lifestyle preferences, and long-term goals. This article will delve into the various advantages and disadvantages of both renting and buying, offering a comprehensive overview to help you navigate this crucial decision-making process. Understanding the nuances of each option is crucial for making an informed choice that aligns with your specific needs and aspirations, whether you are a first-time homebuyer, seasoned investor, or simply looking for the best housing solution.
From the flexibility and lower upfront costs associated with renting to the potential for building equity and long-term financial stability that comes with buying a home, each option presents its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks. Exploring the pros and cons of renting vs buying is essential to making a sound financial decision. We will examine key factors such as market conditions, affordability, maintenance responsibilities, and investment potential, empowering you to confidently determine whether renting or buying is the right choice for you in the current real estate landscape.
Financial Flexibility vs Investment
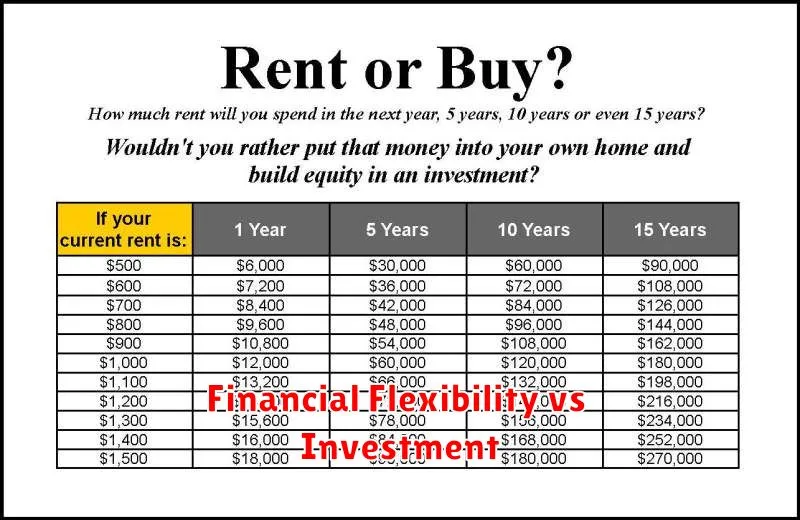
A key differentiator between renting and buying lies in financial flexibility versus long-term investment. Renting typically requires a lower upfront financial commitment. Security deposits and first/last month’s rent are generally less than a down payment on a house. This provides greater financial flexibility, allowing renters to relocate more easily for career opportunities or lifestyle changes.
Homeownership, conversely, is often viewed as a long-term investment. While a significant upfront investment is required, mortgage payments build equity over time. Real estate appreciation can further increase the value of the property, potentially leading to substantial returns upon sale. However, this investment comes at the cost of reduced flexibility, as selling a home can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Responsibility for Repairs
A key difference between renting and buying lies in who is responsible for repairs. When renting, the landlord typically bears the responsibility for most repairs, especially structural or system-related issues like plumbing or heating. This can offer a significant advantage for renters, relieving them of the financial and logistical burden of home maintenance.
However, renters may be responsible for minor repairs or damage caused by their negligence. It’s crucial to carefully review the lease agreement to understand the specific responsibilities of both the landlord and tenant.
Homeowners, on the other hand, assume full responsibility for all repairs, both big and small. This can translate into substantial expenses, requiring homeowners to budget for unexpected maintenance and repairs. While this can be a significant financial commitment, it also grants homeowners complete control over the property and the ability to customize repairs and upgrades as they see fit.
Freedom to Relocate
One of the most significant advantages of renting is the flexibility it offers regarding relocation. Lease agreements typically span one year, providing a defined timeframe for residency. This makes it considerably easier to move to a new city for a job opportunity, a change of scenery, or any other reason, without the burden of selling a property.
In contrast, homeowners face a more complex process when relocating. Selling a home can take months, requiring significant effort in preparing the property for sale, listing it, showing it to potential buyers, negotiating offers, and finally closing the deal. Market conditions can also significantly impact the time and ease of selling a home.
Renters can simply fulfill their lease obligations and move on, while homeowners must navigate the often time-consuming and unpredictable real estate market.
Equity Building in Ownership

One of the most significant advantages of homeownership is the opportunity to build equity. Equity represents the portion of your home that you actually own outright. As you make mortgage payments, a portion of each payment goes towards reducing the principal balance of your loan, increasing your equity over time.
Additionally, property values tend to appreciate over the long term, further contributing to equity growth. This accumulated equity can be a valuable financial asset, acting as a forced savings plan and providing potential access to funds through refinancing or a home equity loan. This can be used for major expenses like home improvements, education, or investments.
Which Is Right for You?
Deciding between renting and buying a home is a significant financial decision. The “right” choice depends entirely on your individual circumstances and priorities.
Financial Stability plays a key role. Buying requires a significant upfront investment (down payment, closing costs) and ongoing expenses (mortgage, property taxes, maintenance). Renting typically has lower upfront costs but offers less long-term financial gain.
Flexibility is another important factor. Renting offers greater flexibility to relocate. Buying ties you to a location, making it less ideal for those anticipating moves.
Your lifestyle should also be considered. Homeownership requires commitment to maintenance and repairs. Renting often shifts these responsibilities to the landlord.
Finally, consider your long-term goals. Buying builds equity and can be a valuable long-term investment. Renting provides housing without the responsibilities of ownership.

